This inheritance list is sorted roughly, but not completely, alphabetically:
[detail level 123]
| Ccaffe::Batch< Dtype > | |
| Ccaffe::Blob< Dtype > | A wrapper around SyncedMemory holders serving as the basic computational unit through which Layers, Nets, and Solvers interact |
| Ccaffe::Blob< int > | |
| Ccaffe::Blob< unsigned int > | |
| Ccaffe::BlockingQueue< T > | |
| Ccaffe::BlockingQueue< caffe::Batch< Dtype > *> | |
| Ccaffe::Caffe | |
| Ccaffe::Net< Dtype >::Callback | |
| Ccaffe::Solver< Dtype >::Callback | |
| Ccaffe::db::Cursor | |
| Ccaffe::DataTransformer< Dtype > | Applies common transformations to the input data, such as scaling, mirroring, substracting the image mean.. |
| Ccaffe::db::DB | |
| ▼Ccaffe::Filler< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with constant or randomly-generated data |
| Ccaffe::BilinearFiller< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with coefficients for bilinear interpolation |
| Ccaffe::ConstantFiller< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with constant values 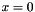 |
| Ccaffe::GaussianFiller< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with Gaussian-distributed values 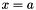 |
| Ccaffe::MSRAFiller< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with values 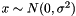 where where 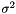 is set inversely proportional to number of incoming nodes, outgoing nodes, or their average is set inversely proportional to number of incoming nodes, outgoing nodes, or their average |
| Ccaffe::PositiveUnitballFiller< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with values ![$ x \in [0, 1] $](form_3.png) such that such that 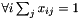 |
| Ccaffe::UniformFiller< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with uniformly distributed values 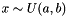 |
| Ccaffe::XavierFiller< Dtype > | Fills a Blob with values 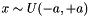 where where 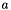 is set inversely proportional to number of incoming nodes, outgoing nodes, or their average is set inversely proportional to number of incoming nodes, outgoing nodes, or their average |
| Ccaffe::Caffe::RNG::Generator | |
| ▼Ccaffe::InternalThread | |
| ►Ccaffe::BasePrefetchingDataLayer< Dtype > | |
| ▼Ccaffe::Layer< Dtype > | An interface for the units of computation which can be composed into a Net |
| Ccaffe::AccuracyLayer< Dtype > | Computes the classification accuracy for a one-of-many classification task |
| Ccaffe::ArgMaxLayer< Dtype > | Compute the index of the 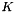 max values for each datum across all dimensions max values for each datum across all dimensions 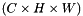 |
| ►Ccaffe::BaseConvolutionLayer< Dtype > | Abstract base class that factors out the BLAS code common to ConvolutionLayer and DeconvolutionLayer |
| ►Ccaffe::BaseDataLayer< Dtype > | Provides base for data layers that feed blobs to the Net |
| Ccaffe::BatchNormLayer< Dtype > | Normalizes the input to have 0-mean and/or unit (1) variance across the batch |
| Ccaffe::BatchReindexLayer< Dtype > | Index into the input blob along its first axis |
| Ccaffe::BiasLayer< Dtype > | Computes a sum of two input Blobs, with the shape of the latter Blob "broadcast" to match the shape of the former. Equivalent to tiling the latter Blob, then computing the elementwise sum |
| Ccaffe::ConcatLayer< Dtype > | Takes at least two Blobs and concatenates them along either the num or channel dimension, outputting the result |
| Ccaffe::CropLayer< Dtype > | Takes a Blob and crop it, to the shape specified by the second input Blob, across all dimensions after the specified axis |
| Ccaffe::DummyDataLayer< Dtype > | Provides data to the Net generated by a Filler |
| Ccaffe::EltwiseLayer< Dtype > | Compute elementwise operations, such as product and sum, along multiple input Blobs |
| Ccaffe::EmbedLayer< Dtype > | A layer for learning "embeddings" of one-hot vector input. Equivalent to an InnerProductLayer with one-hot vectors as input, but for efficiency the input is the "hot" index of each column itself |
| Ccaffe::FilterLayer< Dtype > | Takes two+ Blobs, interprets last Blob as a selector and filter remaining Blobs accordingly with selector data (0 means that the corresponding item has to be filtered, non-zero means that corresponding item needs to stay) |
| Ccaffe::FlattenLayer< Dtype > | Reshapes the input Blob into flat vectors |
| Ccaffe::HDF5DataLayer< Dtype > | Provides data to the Net from HDF5 files |
| Ccaffe::HDF5OutputLayer< Dtype > | Write blobs to disk as HDF5 files |
| Ccaffe::Im2colLayer< Dtype > | A helper for image operations that rearranges image regions into column vectors. Used by ConvolutionLayer to perform convolution by matrix multiplication |
| Ccaffe::InnerProductLayer< Dtype > | Also known as a "fully-connected" layer, computes an inner product with a set of learned weights, and (optionally) adds biases |
| Ccaffe::InputLayer< Dtype > | Provides data to the Net by assigning tops directly |
| ►Ccaffe::LossLayer< Dtype > | An interface for Layers that take two Blobs as input – usually (1) predictions and (2) ground-truth labels – and output a singleton Blob representing the loss |
| Ccaffe::LRNLayer< Dtype > | Normalize the input in a local region across or within feature maps |
| Ccaffe::LSTMUnitLayer< Dtype > | A helper for LSTMLayer: computes a single timestep of the non-linearity of the LSTM, producing the updated cell and hidden states |
| Ccaffe::MVNLayer< Dtype > | Normalizes the input to have 0-mean and/or unit (1) variance |
| ►Ccaffe::NeuronLayer< Dtype > | An interface for layers that take one blob as input ( 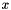 ) and produce one equally-sized blob as output ( ) and produce one equally-sized blob as output ( 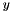 ), where each element of the output depends only on the corresponding input element ), where each element of the output depends only on the corresponding input element |
| Ccaffe::ParameterLayer< Dtype > | |
| Ccaffe::PoolingLayer< Dtype > | Pools the input image by taking the max, average, etc. within regions |
| Ccaffe::PythonLayer< Dtype > | |
| ►Ccaffe::RecurrentLayer< Dtype > | An abstract class for implementing recurrent behavior inside of an unrolled network. This Layer type cannot be instantiated – instead, you should use one of its implementations which defines the recurrent architecture, such as RNNLayer or LSTMLayer |
| Ccaffe::ReductionLayer< Dtype > | Compute "reductions" – operations that return a scalar output Blob for an input Blob of arbitrary size, such as the sum, absolute sum, and sum of squares |
| Ccaffe::ReshapeLayer< Dtype > | |
| Ccaffe::ScaleLayer< Dtype > | Computes the elementwise product of two input Blobs, with the shape of the latter Blob "broadcast" to match the shape of the former. Equivalent to tiling the latter Blob, then computing the elementwise product. Note: for efficiency and convenience, this layer can additionally perform a "broadcast" sum too when bias_term: true is set |
| Ccaffe::SilenceLayer< Dtype > | Ignores bottom blobs while producing no top blobs. (This is useful to suppress outputs during testing.) |
| Ccaffe::SliceLayer< Dtype > | Takes a Blob and slices it along either the num or channel dimension, outputting multiple sliced Blob results |
| Ccaffe::SoftmaxLayer< Dtype > | Computes the softmax function |
| Ccaffe::SplitLayer< Dtype > | Creates a "split" path in the network by copying the bottom Blob into multiple top Blobs to be used by multiple consuming layers |
| Ccaffe::SPPLayer< Dtype > | Does spatial pyramid pooling on the input image by taking the max, average, etc. within regions so that the result vector of different sized images are of the same size |
| Ccaffe::TileLayer< Dtype > | Copy a Blob along specified dimensions |
| Ccaffe::LayerRegisterer< Dtype > | |
| Ccaffe::LayerRegistry< Dtype > | |
| Ccaffe::Net< Dtype > | Connects Layers together into a directed acyclic graph (DAG) specified by a NetParameter |
| Ccaffe::Caffe::RNG | |
| Ccaffe::SignalHandler | |
| ▼Ccaffe::Solver< Dtype > | An interface for classes that perform optimization on Nets |
| ►Ccaffe::SGDSolver< Dtype > | Optimizes the parameters of a Net using stochastic gradient descent (SGD) with momentum |
| Ccaffe::SolverRegisterer< Dtype > | |
| Ccaffe::SolverRegistry< Dtype > | |
| Ccaffe::BlockingQueue< T >::sync | |
| Ccaffe::SyncedMemory | Manages memory allocation and synchronization between the host (CPU) and device (GPU) |
| ▼Ccaffe::Timer | |
| Ccaffe::CPUTimer | |
| Ccaffe::db::Transaction |
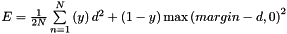 where
where 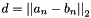 . This can be used to train siamese networks
. This can be used to train siamese networks 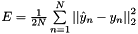 for real-valued regression tasks
for real-valued regression tasks ![$ E = \frac{-1}{n} \sum\limits_{n=1}^N \left[ p_n \log \hat{p}_n + (1 - p_n) \log(1 - \hat{p}_n) \right] $](form_163.png) , often used for predicting targets interpreted as probabilities
, often used for predicting targets interpreted as probabilities 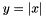
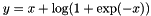 if
if 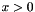 ;
; 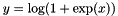 otherwise
otherwise 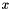 to 0, adjusting the rest of the vector magnitude accordingly
to 0, adjusting the rest of the vector magnitude accordingly 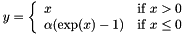
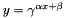 , as specified by the scale
, as specified by the scale 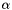 , shift
, shift 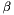 , and base
, and base 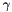
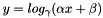 , as specified by the scale
, as specified by the scale 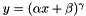 , as specified by the scale
, as specified by the scale 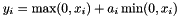 . The differences from
. The differences from 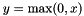 . The simple max is fast to compute, and the function does not saturate
. The simple max is fast to compute, and the function does not saturate 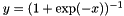 , a classic choice in neural networks
, a classic choice in neural networks 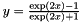 , popular in auto-encoders
, popular in auto-encoders  1.8.13
1.8.13